A rare radiation, dangerous, penetrating, difficult to absorb
The neutron radiation is more penetrating than alpha and beta . It is more dangerous than gamma rays. It is fortunately short-lived and rarely encountered. Its exposure is exceptional: intervention in the core of a reactor, critical accident, and at a different scale, exploding atomic bomb or hydrogen bomb (in an hydrogen bomb neutrons are produced through the deuterium-tritium reaction).
Under normal circumstances, exposure is reduced to a few neutrons produced by cosmic radiation. It is very low.
In an atomic explosion, the neutron radiation is particularly harmful. But the neutronic flash does not last. Free neutrons have an half-life of 12 minutes. They are generally absorbed by matters before decaying.
In the 80s, low-power atomic bombs were developed, without blast – so not destructing – but releasing an instantaneous neutron flux of fatal intensity. These « neutron bombs » were intended to annihilate enemy combatants, while allowing to occupy the ground shortly after. After widespread protests in public opinion at the time, these weapons were in principle abandoned.
In practice, it is in the vicinity of reactors and accelerators in certain research laboratories that protection against neutrons needs to be implemented because of high neutron fluxes.
Neutrons, slowed down by multiple collisions with the encountered material nuclei, are quickly captured. Generally capture is followed by a de-excitation gamma radiation of which we must be protected. It should also be remembered that part of the captures produced radioactive nuclei. The effects of this radioactivity diluted over time, continue to occur after neutron absorption.
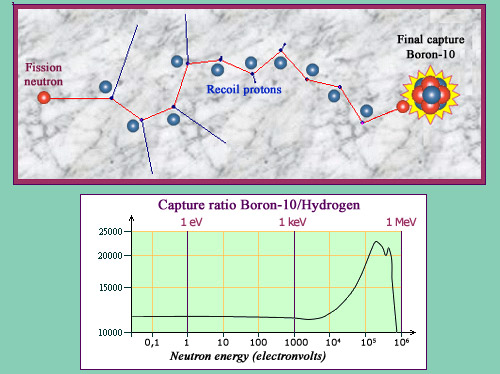
The boron neutron trap
In order to protect against neutron produced in reactors, one add boron to the concrete composition of the surrounding containment walls. The curve shows that the probability of neutron capture by a nucleus of boron-10 (a naturally occurring isotope of boron) exceeds more than 10 000 times that of a hydrogen nucleus. But if ratios barely vary, the boron capture probabilities greatly increase when the neutron slows down. There is sharing of roles: the protons of hydrogen from water slow the neutrons by collisions until they are captured by boron. To make them visible on the upper diagram, protons recoils have been magnified.
© IN2P3 (Source Janis data base)
At last neutrons are captured by the nuclei. To protect oneself, the most effective way is to make such catches, by incorporating in the shielding material nuclei greedy of neutrons. The probabilities of capture of slow neutrons become very important for nuclei such as boron-10 and cadmium. The nucleus becomes very large, as a goalkeeper with sprawling arms.
One protects oneself from neutrons by incoporating boron in the concrete containment enclosure of reactors. Concrete contains water, therefore hydrogen that effectively slows down the neutrons. Boron incorporated in the concrete contains 20% boron-10 a boron isotope very effective in capturing neutrons. For slow neutrons, this nucleus looks 60 times bigger than its actual size. Cadmium is also used for reactors control rods, its capture probability (cross-section) of 2000 barns beeing 200 times that of Iron (10 barns).
In the case of fissile material, one should avoid the risk of criticality, that is to say, the unexpected development of chain reactions. For example in the storage pools, the spent fuel assemblies that contain a further 1% fissionable uranium are separated and placed in steel baskets containing boron.
Other articles on the subject « Radioprotection »
Radioprotection principles
Applying common sense rules according to radiation nature The need for protection from radiation [...]
Gamma Radioprotection
A penetrative radiation more difficult to absorb In the case of ingestion of radioactive substanc[...]
Gamma Attenuation
Attenuation of a gamma beam Of the three types of radiations, gamma rays are the most penetrative[...]
Gamma Absorption
Heavy materials for the absorption of gamma rays In terms of radioprotection mitigate gamma rays [...]
Radioactive Decontamination
Avoid all contact, ingestion and inhalation One of the tasks of radiation protection is the decon[...]
Justification and optimisation
In medicine, use of radiation must be justified The ‘Justification and Optimization » princ[...]
Reglementations and controls
Strict regulations for an efficient radioprotection Radioprotection has a long history. Its princ[...]
Dose legal limits
Applying the precautionary principle and setting cautious limits French regulations set at 1 mSv [...]
Actors in radioprotection
The actors and the basics of radioprotection regulations The rules of radiation protection are no[...]