A direct-reading dosimeter for monitoring X-ray and gamma doses
The pen dosimeter consists of an ionization chamber, usually cylindrical and about the size of a large pen, crossed by a quartz-fiber anode wire connected to a charged capacitor and an electrometer used to measure its discharge.
An optical system allows the user to visualize the deflection of the fiber and thus directly read the received dose.
Resetting is performed by recharging the capacitor.
The direct reading allows, at any time, to know the amount of X-ray or gamma radiation absorbed since the last recharge.
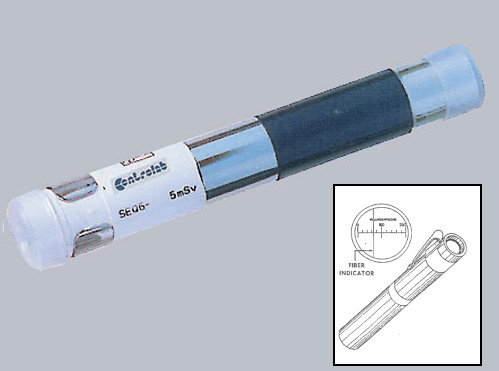
Pen dosimeter used for work involving radiation exposure
The pen dosimeter is a device that allows, by simple visual reading, the monitoring of the absorbed dose received during a task carried out in the presence of ionizing radiation.
The principle of determining X and gamma radiation doses is based on the discharge, under the action of radiation, of an electroscope initially charged by an external voltage source of about 200 V.
A graduated eyepiece micrometer allows the reading.
© Controlab
Pen dosimeters exist in various sensitivities, measuring absorbed doses ranging from 1, 2, 5, 10, and 50 milligrays (mGy) up to 2
grays (Gy).
The pen dosimeter is used in addition to personal dosimeters such as film badges or thermoluminescent dosimeters, which provide a more accurate measurement of the absorbed dose, but only a posteriori.
This device has the advantage of being readable at any time, directly at the workplace.
Depending on the materials used for the chamber wall, it is sensitive to different energies or types of radiation.
Its relatively simple design makes it a robust and reliable device, although somewhat fragile.
It provides continuous monitoring of working conditions through direct reading, helping to prevent potentially dangerous exposures.
Less precise than film badges, however, the pen dosimeter is not suitable for widespread use.
See also:
Principles of detection
Absorbed doses