Investigations of the cardiac muscle functionning
MYOCARDIAL SCINTIGRAPHY BY PERFUSION
Principle and test implementation
Myocardial scintigraphy by perfusion can assess blood flow to the heart muscle (evaluation of the infusion) and provides information on its function and capabilities of contraction.
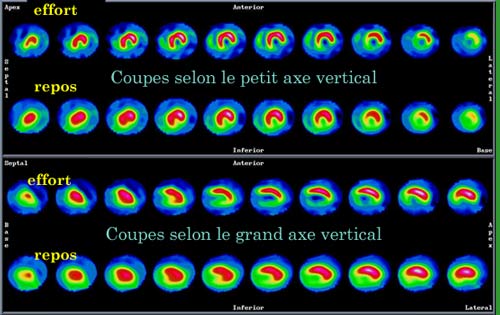
Myocardial scintigraphy
Myocardial scintigraphy is designed to assess blood flow in the heart muscles (perfusion assessment) and provide information on its mechanism. It is estimated by operating through tomographic section of cardiac volume done according to three planes, then comparing the acquisitions made after an exercise test and during rest. Here we see two of the plan sections made known as « small vertical » and « large vertical” axis.
© CHU Avicenne
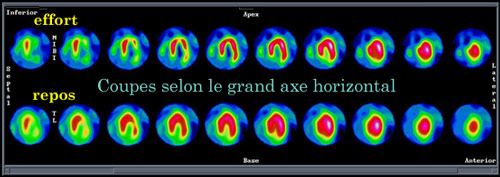
Myocardial scintigraphy: large horizontal axis sections
Completing the previous diagrams of the same cardiac test , this set shows sections of the heart according to the third plane, the transverse plane. A doctor who makes a diagnostic gets an access to three sets of sections at the same time.
© CHU Avicenne
The comparison of the radiotracer fixation in the heart muscle for two situations, one during effort and one at rest is used to diagnose or exclude heart disease.
The first phase of the review is therefore to perform a stimulation test (effort on bicycle and / or pharmacological test) to assess cardiac perfusion under stress. At the end of stimulation the radiopharmaceutical is injected intravenously and an tomographic acquisition under multiple angles is completed.
The second phase of the examination is performed 3-4 hours after the acquisition effort to evaluate the cardiac perfusion at rest.
Today, more and more sensitive detectors offer the possibility to multiply scintigraphic cross-sections without increasing the dose of exposure. Thanks to the progress of computing power, one can go from planar images to an image in space. Doctors now have on their screens animated sequences that, bringing together these multiple images, film heartbeats and highlight possible anomalies.
Indications of cardiac scintigraphy by perfusion:
– Myocardial infarct: diagnosis, localization and extent of necrosis, looking for residual ischemia;
– Coronary artery: diagnosis, assessment and monitoring;
– Cardiomyopathies: differential diagnosis, prognosis.
Radiopharmaceuticals most frequently used:
– Thallium-201 (201Tl) period 72 hours ;
– Technetium-99m (Tc99m MIBI) period 6 hours.
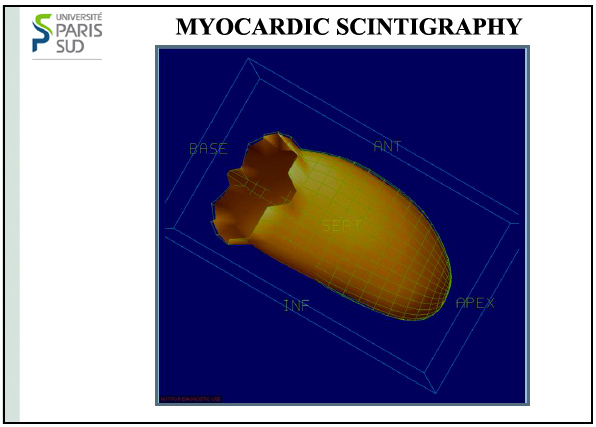
Tomoscintigraphy of the myocard muscle
The heart is a muscle whose beats are periodic. Scintigraphies corresponding to a given moment of the cardiac cycle can be made. From scintigraphies made at different angles, heart momenttomoscintigraphies can be reconstructed and combined with scanner information. From these reconstructions, the heart behavior can be displayed during a beat thanks to computer techniques.
© Université Paris-Sud
ISOTOPIC VENTRICULOGRAPHY
Principle and test implementation
The ventriculography with radionuclide allows the analysis of the volume of cardiac cavities (normal or dilated),and of its global or segmental contractility (ejection fraction).
Main indication of radionuclide ventriculography:
– Measurement of left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF)
Radiopharmaceuticals used:
– Albumin tagged with Technetium-99m
– Marking of erythrocytes (pyrophosphate technetium-99m pertechnetate +)
Other articles on the subject « Scintigraphic examinations »
Nuclear Scintigraphies
A range of diagnoses for determining how the body works … The word ‘scintigraphy&lsqu[...]
Scintigraphic Diagnostics
A tool for non-aggressive analyses of biological functions Diseases are biological processes and [...]
Indications for Scintigraphy
When to Use Scintigraphy? The nuclear medicine physician must choose the appropriate marker produ[...]
Bone Scintigraphies
Principle and implementation of bone scintigraphies Bone scintigraphy is based on the fixation in[...]