A variety of designs : Natural uranium or enriched uranium as fuel
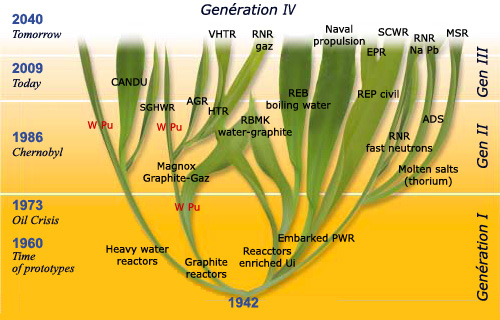
Genealogy of reactors
The family tree has branches extinct or nearly extinct, while others are vigorous or emerging. The six Generation IV designs appear at the top of the tree: (V)HTR (very) high temperature reactors; SCWR supercritical water reactors ; FBR sodium or lead cooled Fast Breeder Reactors; MSR Molten Salt Reactor. Which will expand? Some other abreviations: PWR pressurized water reactor ; WPu Weapon-grade plutonium reactor ; CANDU Canadian reactors, using natural uranium, cooled and moderated by heavy water ; Magnox and Advanced gas-cooled reactor (AGR) UK graphite moderated reactors,: ADS Accelerator Driven Systems.
@ CEA/DEN
There are several industrial techniques currently used to produce electricity from nuclear fission. These different techniques are referred to as ‘reactor families » or « reactor brands‘. Each brand of reactors corresponds to the choice of a few essential parameters or options.
The most important is the choice of the fuel and its degree of enrichment in fissile isotopes. This degree determines the type of neutrons, slow or fast, involved in the fission reactions. Uranium fuel, natural moderately enriched in uranium-235, will require a moderator to slow neutrons, whereas reactors with fuel rich in fissile isotopes (U-235 or Pu-239) operate with fast neutrons. Today all nuclear power plants (NPP) are fuelled by uranium: whether natural, enriched, or containing a part of fissile plutonium-239.
For slow neutron reactors, there also has to be a choice of the moderator – the material which slows the neutrons down – which is either graphite, heavy water or ordinary water. There are no moderator in fast neutron reactors.
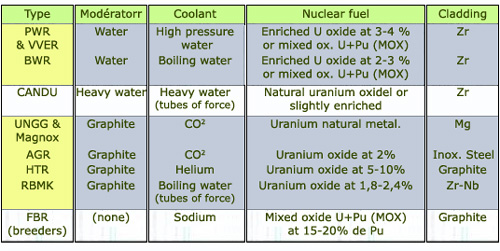
Main characteristics and options of reactor families
Commercial reactors operate with natural or moderately enriched uranium. Using natural uranium as fuel restricts the choice of moderator to graphite and heavy water. The use of enriched uranium opens a large choice of coolant (liquid, vapor or gas) and moderators. Some combinations are more successful than others: water, either heavy or ordinary, has been successful since it is an efficient coolant and a good moderator. Light water reactors (PWRs and BWRs) represent the majority of today Generation II reactors and their Generation III successors.
@ P.Reuss/Précis de neutronique EDP Sciences 2003
In order to evacuate the heat away from the reactor core, the coolant should be an efficient heat conveying-medium not to greedy in capturing neutrons. This ‘heat conveying fluid‘ plays sometimes also the part of moderator. This is the case with heavy or ordinary light water, which can be boiling or under pressure. The coolant can be gaseous (pressurized carbon dioxide or helium) or even a molten metal like molten sodium or lead in the case of fast neutrons reactors.
There are other important technical parameters, such as the layout of the fuel in the reactor’s core with respect to the coolant and moderator, the fuel cladding and its packaging , the nature and number of heat exchangers.
Some reactors, the first to be developed after the Second World War, are for military use. It was less to produce electricity to obtain weapon-grade plutonium for weapons. These ‘plutonigenous” reactors gave birth to civilian reactors using natural uranium as fuel and heavy water or graphite as moderator.
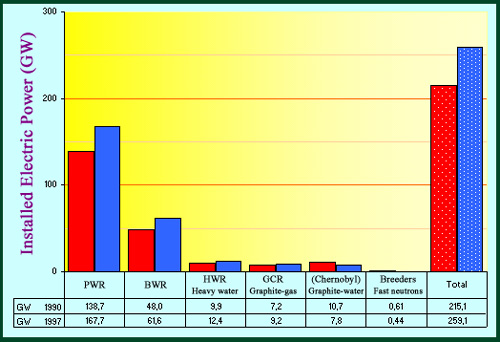
Prevalence of pressurized water reactors PWR
The distribution of electric power installed in 1990 and 1997 shows the predominance of pressurized water reactors (PWR), followed by that of boiling water reactors (BWR). This distribution has changed little since. The production of electricity from fast neutron or breeder reactors remains marginal until the proposed arrival of 2040 Generation IV reactors.
@ IN2P3
Dominance of light water reactors (LWR)
The repartition of the installed electrical power is characterized by the overwhelming predominance of light water reactors operating with enriched uranium. The graphite reactors are disappearing. Among the natural uranium reactors, only the Canadian family of heavy water CANDU reactors is still well alive.
The family of pressurised water reactors powered by moderately enriched uranium accounts by itself for 60% of the total power produced by nuclear reactors worldwide (80% in Europe). Because of its significance, the PWR family will be discussed in greater detail elsewhere. The promising fast neutron breeders, limited today to a very small number of units but able to extract much more energy from uranium than now, await the possible arrival of Generation IV reactors. The ADS, reactors coupled to a particle accelerator, would play the part of waste burners within the panoply of reactors of the far future.
Other articles on the subject « Nuclear Reactors »
World nuclear reactors
A development that takes place today in Asia At the beginning of 2014 the number of reactors in o[...]
Generation I reactors
1950-1970: First generation of reactors (50 – 500 MWe) The first generation reactors were i[...]
RBMK reactors
Soviet-era reactors at Chernobyl Cold War and the Iron Curtain led after 1947 to the development [...]
Generation II Reactors
1970-2009: the rise of nuclear energy About 85% of electricity produced worldwide by nuclear powe[...]
PWR Reactors
The most widespread type of reactor … Pressurised water reactors (PWR) are by far the most [...]
PWR Operation
High pressure water to evacuate heat and slow down neutrons The reactor core is the source of ene[...]
Boiling Water Reactors
BWR or Boiling Water Reactors Boiling water reactors or BWR are in operation in the United States[...]
Candu reactors
Canadian reactors using natural uranium and heavy water CANDU is a nuclear reactor brand develope[...]
Nuclear Propulsion
On-board reactors for submarines and aircraft carriers In addition to conventional land-based pow[...]