Area 3: Research into conditioning
The conditioning of high-level and intermediate-level waste is one of the two topics being studied in research area 3 under the laws of 1991 and June 2006. The situation in this area is very different from research into partitioning and transmutation. Conditioning has benefited from major industrial advances in the last 15 years.
Major industrial advances
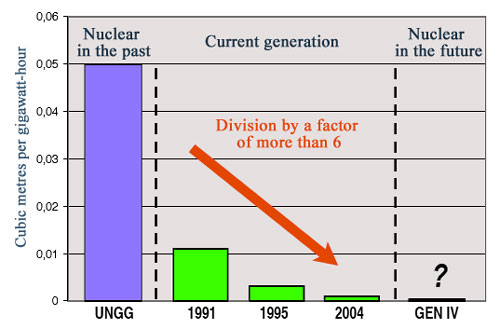
One main advances in the conditioning of waste has been a reduction by a factor of 6 in the volume of high-level long-lived waste (HLW-LL) produced, 15 years after the Bataille Act was passed, from 1991 to 2006. This reduction is even greater by comparison with the first graphite-moderated gas-cooled reactors. Waste volumes are calculated in relation to the amount of electricity produced: one gigawatt-hour, which is equivalent to one million kilowatt-hours.
© CEA
During this period, the volume of high-level waste being produced has fallen by a factor more than 6. Very effective conditioning has been developed for all types of waste: special glass and ceramics for high-level waste, bitumen and cement for intermediate-level waste and bulk containers for very low-level waste. The R7T7 glass produced at La Hague, which is used to immobilise the radioactivity of high-level waste, has a life of more than 10,000 years.
Although excellent results have been achieved, research into conditioning continues and is being extended. Could the ‘put everything in glass’ strategy adopted by France be improved or added to? For example, could more minor actinides be incorporated into R7T7 glass, to take account of the fact that larger quantities of these radioelements are present in spent MOX fuel assemblies? There is also legacy waste that needs to be recovered and conditioned.
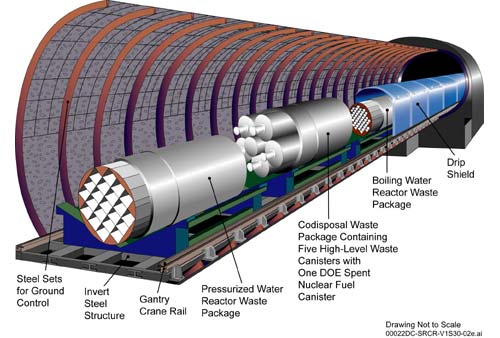
Containers for Yucca Mountain
This gallery for the waste disposal facility project at Yucca Mountain in the Nevada Desert shows three types of waste container: fuel assemblies for pressurized water reactors and boiling water reactors (in the foreground and background), and packages of high-level waste (in the middle). In blue one can see titanium shields used to protect the containers from any water that drips from the ceiling. The site has a desert climate but the layers of tuff (compacted volcanic ash) in Yucca Mountain are not as impermeable as clay. That is one of the reasons why the project was abandoned
© OCRWM/DOE
In the future, when the partitioning becomes possible of radioelements that are currently incorporated into glass in a mix, it will be useful to be able to condition some of these radioelements separately. Researchers are therefore looking at the incorporation of specific radioelements into ceramic matrices. These ceramics are exceptionally water resistant but they are also expensive. Research into these materials in France is grouped together under a programme known as NOMADE (NOuveaux MAtériaux pour DEchets). Ceramics cannot be ruled out as containment materials for specific applications. A comparative study needs to be done of these new conditioning materials and R7T7 glass.
Major research is also being conducted into spent fuel that is not reprocessed. Special packages are necessary for spent fuel that will be stored before burial. Countries that do not reprocess spent fuel, such as Sweden and the US, are giving priority to the development of canisters and containers that can hold in the irradiated materials in fuel assemblies for thousands of years.

Another advance: resistant glass
A major industrial advance is the highly resistant borosilicate glass used at La Hague plant. According to CEA’s estimates, this glass loses only a thousandth of its volume in 10,000 years, and 10% after a million years. The silica dissolved in the water of a geological environment would slow erosion. A protective gel would form, increasing the material’s longevity. After these timescales, the radioactivity would have practically disappeared, if humans are still around to notice it.
© DR
More generally, robust, durable packages that are easy to handle need to be developed for all types of waste. High-level and intermediate-level waste, such as spent fuel that has not been reprocessed, is currently stored before being disposed of for good. This storage is long-term. Only in around 2025 will the first waste from French nuclear power plants in the 1970s start to be put into waste disposal facilities. First the long-term behaviour of the packages has to be checked. They must still be in a good enough condition to be handled once they are taken out of storage.
Other articles on the subject « Waste Outlooks »
Three research areas
Three complementary research areas The three research areas under the Bataille Act, later supplem[...]
Area 1: Partitioning
Sorting the radioelements in radioactive waste The separation, or partitioning, of the radioactiv[...]
Partitioning: results
Development of processes and extractant molecules The 2006 assessment of research into partitioni[...]
Advanced partitioning
Partitioning of nuclear waste: hot chemistry Advanced partitioning goes beyond just the partition[...]
Area 1: Transmutation
Area 1: Transmuting or transforming radioactive atoms Transmutation is the second part of researc[...]
Transmutation facilities
Fast reactors and Accelerator Driven Systems (ADS) The neutron, which easily penetrates nuclei, i[...]
Transmutation prospects
A far away objective for Generation IV and 2040… At the time of the first tests on the tran[...]
Area 2: Disposal
Research into deep geological disposal Can the nuclear industry’s final waste, which we cur[...]
Area 3: Long Surface Storage
Research into long-term storage Research into long-term storage is the second research topic in a[...]
Long surface storage concepts
Long-term surface and subsurface storage Research into very long-term storage is a matter for the[...]