Five categories of radioactive waste
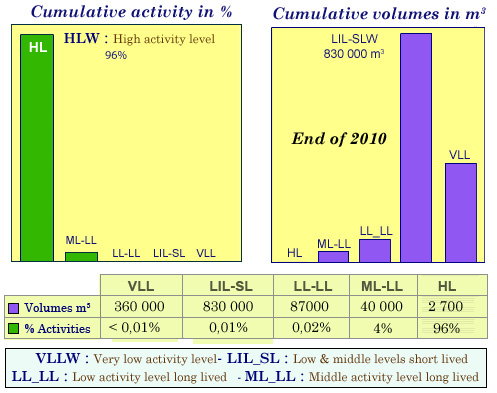
Activity levels and volumes of waste categories
The greater the volume of a waste category, the lower its radioactivity level. This relationship between volume and activity level for the five categories of waste is illustrated by the figure. The diagram on the right shows the accumulated volumes of each type of waste since the start of nuclear program, according to the inventory prepared by ANDRA at the end of 2010. It can be seen that 96% of the radioactivity is concentrated in the ‘high-level waste ‘ category, but the volume represents only 0.2% of the total.
© Souce : ANDRA 2012 Inventory
The level and length of life are the deciding factors when it comes to managing radioactive waste. They are used to classify waste into categories. For each category an inventory is then prepared, and management is adapted to the volume and characteristics.
In France, the French National Radioactive Waste Management Agency (ANDRA) is responsible for carrying out an inventory of all the radioactive materials in France. This inventory includes recoverable materials – uranium and plutonium extracted from the spent fuel from reactors – which are counted separately from the radioactive waste.
Over the years Andra has built up a database of existing waste and its geographical location, mainly from statements made by waste producers and handlers.
In the early 2000s, the scope of the inventory was extended. It now provides a panorama of radioactive waste broken down into families with similar characteristics. It describes the date when it was drawn up, and the state of the waste: conditioned (i.e. in its final form) or not conditioned (pending decisions dependent on the outcome of research). It also prepares an outlook, which forecasts the quantities of waste to be produced in future.
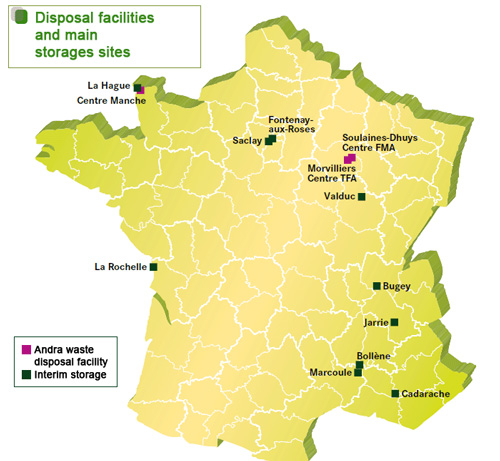
Disposal facilities and storage sites in France
High- and intermediate-level waste covered by the Bataille Act is concentrated at a few sites, including La Hague and Marcoule, where it is stored pending decisions about its future. Research for its disposal is being carried out at Bure in Lorraine. Very low-level waste and low- and intermediate-level short-lived waste, which presents few risks, are already disposed definitively at three sites at Morvilliers, the Manche facility and Soulaines. There are also other smaller storage sites, some of them military.
© ANDRA
Waste is classified into categories on the basis of its activity level and the life of its main radioelements. For technical management reasons, ANDRA uses waste groupings. With very low-level waste (VLLW), it does not matter whether the waste is short-lived or long-lived. With short-lived waste, low- and intermediate-level waste (LILW-SL) is combined because the radioactivity disappears relatively quickly. With high-level waste (HLW), generally no distinction is made between short-lived and long-lived waste.
With these groups, the main categories of waste are as follows:
– VLLW: Very low-level waste
– LILW-SL: Low- and intermediate-level short-lived waste
– ILW-LL: Intermediate-level long-lived waste
– HLW: High-level waste including long-lived waste
– LLW-LL: Low-level long-lived waste
The French inventory does not yet include the vast amounts of mining waste managed on the sites of uranium mines, military waste or future waste from dismantling nuclear plants.
In the US, the management of high-level waste is very different. Spent fuel from reactors is currently left on the sites of the nuclear plants until there is a disposal facility that can take it; in France most of this waste is conditioned and grouped at La Hague and Marcoule.
Other articles on the subject « Waste Inventory »
France: waste panorama (1)
An overview of French waste categories… In France, radioactive waste is split into five cat[...]
France: waste panorama (2)
An overview of French waste categories (continued)… Low- and intermediate-level short-lived[...]
US panorama
The case of the greatest nuclear power Nuclear-powered US Navy vessels, past production of nuclea[...]
Various radioactive waste
Radioactive waste from many different sources… When radioactive waste is mentioned, people [...]
Mining residues
Waste from uranium extraction The residues from processing uranium ores are disposed of on the si[...]
Medicine and research
Radioactive sources, producers of waste outside the nuclear industry… Biology labora[...]
Military waste
A separate system Using the gaseous diffusion process, the AREVA Pierrelatte facility produced en[...]
Radium-bearing waste
Legacy waste – weakly radioactive but long-lived Recent and less recent industrial activities hav[...]
Waste from Dismantling
Dismantling of facilities: graphite waste Experience with dismantling nuclear power plants is onl[...]
Waste from Industry
Obsolete radioactive sources, the legacy of radium applications There are numerous industrial app[...]